What causes hot flashes at night – Welcome to our exploration of the enigmatic world of hot flashes at night. This phenomenon, often associated with menopause, can be a disruptive and uncomfortable experience. Let’s delve into the underlying causes and uncover the factors that contribute to this nocturnal discomfort.
Our journey will take us through the intricate workings of the hormonal system, the role of the nervous system, and the impact of environmental triggers. We’ll also explore the connection between sleep disturbances and hot flashes, and discuss the importance of seeking medical attention to rule out any underlying health issues.
Hormonal Changes: What Causes Hot Flashes At Night

During menopause, the ovaries gradually stop producing the hormones estrogen and progesterone. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating body temperature. Estrogen helps to keep blood vessels dilated, which allows for better heat dissipation. Progesterone, on the other hand, helps to maintain a stable body temperature.
As estrogen levels decline during menopause, the blood vessels become narrower, reducing heat dissipation. This can lead to a sudden increase in body temperature, resulting in a hot flash.
Role of Estrogen
- Estrogen helps to dilate blood vessels, allowing for better heat dissipation.
- Estrogen levels decline during menopause, leading to narrower blood vessels and reduced heat dissipation.
Role of Progesterone, What causes hot flashes at night
- Progesterone helps to maintain a stable body temperature.
- Progesterone levels also decline during menopause, contributing to hot flashes.
Nervous System Activity
The nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature, with the hypothalamus acting as the central thermostat. The hypothalamus monitors core body temperature and triggers physiological responses to maintain a stable internal environment.
Hypothalamic Imbalances
When the hypothalamus detects a rise in core body temperature, it initiates mechanisms to cool the body, such as sweating and vasodilation. However, imbalances in the hypothalamus can disrupt this thermoregulation process, leading to hot flashes. These imbalances can be caused by various factors, including hormonal changes during menopause, certain medications, and medical conditions affecting the nervous system.
Sleep Disturbances
The frequency and intensity of hot flashes are closely linked to poor sleep quality. During menopause, hormonal fluctuations can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia, fragmented sleep, and early morning awakenings.
Circadian Rhythm Disruption
Menopause causes a decline in estrogen levels, which plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s circadian rhythm. Estrogen helps maintain the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, but its reduction during menopause can disrupt this rhythm, leading to difficulty falling or staying asleep.
Night Sweats
Hot flashes, particularly night sweats, can significantly disrupt sleep. The sudden onset of intense heat and sweating can awaken individuals from sleep, making it difficult to fall back asleep.
Sleep Fragmentation
The combination of hot flashes and disrupted sleep patterns can lead to sleep fragmentation. Frequent awakenings throughout the night reduce the amount of quality sleep, resulting in fatigue and daytime sleepiness.
Environmental Factors
Environmental triggers can play a significant role in exacerbating hot flashes, especially during the night. Understanding these factors and implementing strategies to manage them can help reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
Heat and Humidity
- Extreme heat and high humidity can trigger hot flashes.
- Staying in cool, well-ventilated areas or using air conditioning can help mitigate these triggers.
- Consider using fans or opening windows to improve air circulation and reduce heat buildup.
Stress
Stress is a known trigger for hot flashes. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress levels and potentially reduce the occurrence of hot flashes.
Certain Foods
- Spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can increase body temperature and trigger hot flashes.
- Avoiding or limiting the consumption of these foods, especially before bedtime, can help reduce hot flashes at night.
Medical Conditions
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/are-night-sweats-a-symptom-of-cancer-514441-01-4a6b98d179c5404e89cc28d09e8928de.png)
Hot flashes can also be a symptom of underlying medical conditions. It’s important to seek medical attention to rule out any serious health issues.
Some medical conditions that can contribute to hot flashes include:
Thyroid Disorders
- An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can cause increased metabolism, leading to hot flashes.
- An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can cause decreased metabolism, which can also lead to hot flashes.
Infections
Certain infections, such as the flu or pneumonia, can cause fever and chills, which can trigger hot flashes.
Lifestyle Factors
Various lifestyle choices can influence the frequency and intensity of hot flashes experienced during menopause. Understanding these factors and making necessary adjustments can help manage these symptoms effectively.
The following table Artikels some common lifestyle factors that may contribute to hot flashes and provides recommendations for minimizing their impact:
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Hot Flashes | Recommended Adjustments | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise | Regular exercise can increase blood flow and body temperature, potentially triggering hot flashes. | Exercise in cooler environments, wear loose-fitting clothing, and stay hydrated. | Helps regulate body temperature and reduce overall stress levels. |
| Diet | Certain foods, such as spicy or caffeine-rich items, can act as triggers for hot flashes. | Identify and avoid trigger foods, maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. | Supports overall well-being and reduces inflammation, which can contribute to hot flashes. |
| Smoking | Nicotine constricts blood vessels, which can worsen hot flashes. | Quit smoking or reduce nicotine intake. | Improves cardiovascular health and reduces the risk of various health conditions, including hot flashes. |
Treatment Options
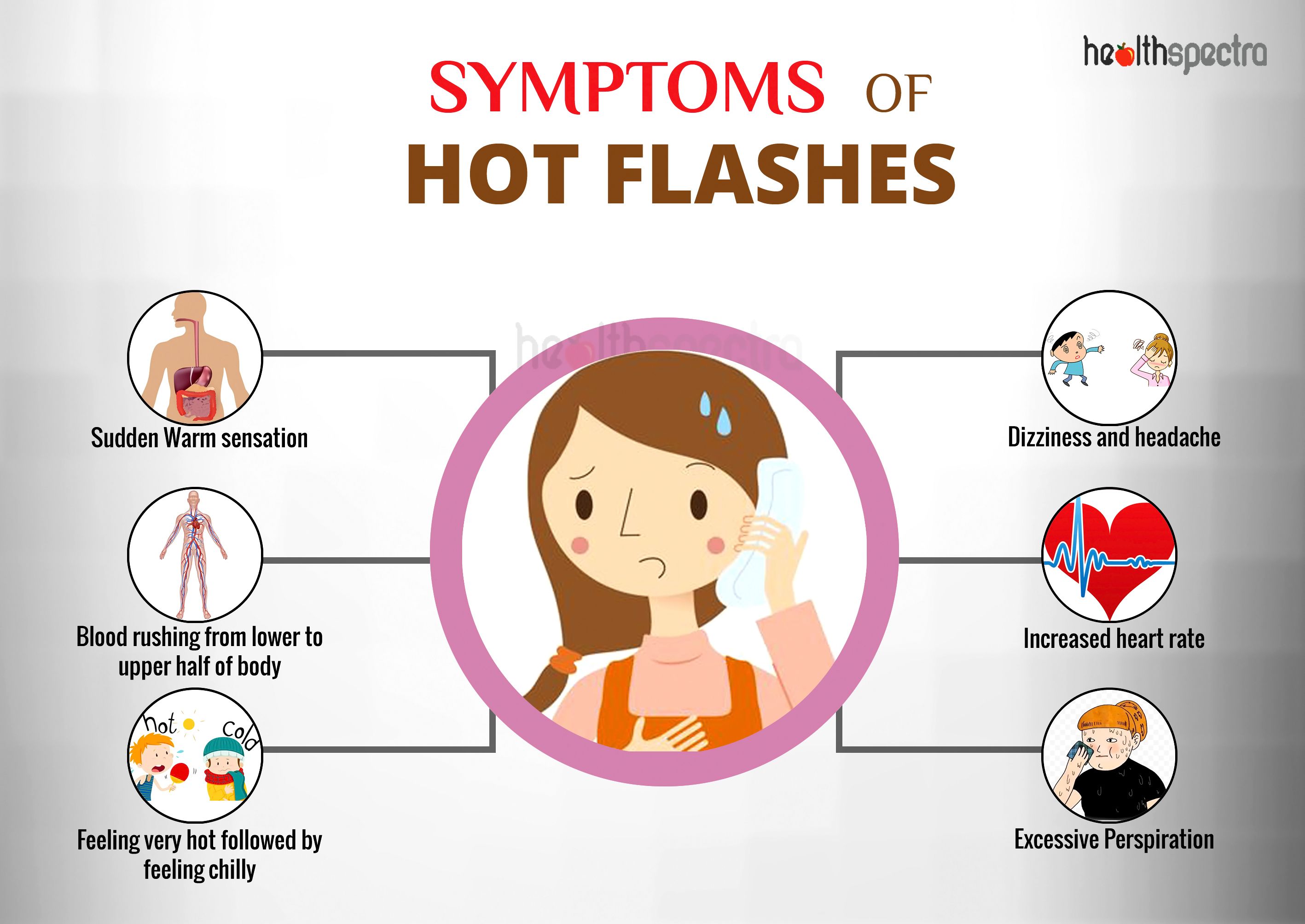
Hot flashes can significantly impact daily life, leading to discomfort, sleep disturbances, and diminished quality of life. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to manage these symptoms effectively.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, individual preferences, and underlying health conditions. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Hormone Therapy
- Benefits:Hormone therapy, particularly estrogen replacement therapy (ERT), can effectively reduce hot flash frequency and severity by replenishing estrogen levels.
- Risks:ERT may increase the risk of certain health conditions, such as breast cancer, blood clots, and heart disease. Therefore, it is crucial to weigh the potential benefits and risks before initiating treatment.
Medication
- Benefits:Non-hormonal medications, such as antidepressants and anticonvulsants, can be effective in managing hot flashes. These medications work by regulating neurotransmitters involved in temperature regulation.
- Risks:Potential side effects of non-hormonal medications include nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Benefits:Lifestyle modifications can complement other treatment options or be effective on their own for managing mild hot flashes. These modifications include:
- Managing stress:Stress can trigger hot flashes. Techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
- Maintaining a healthy weight:Excess weight can contribute to hot flashes. Losing weight, if necessary, can help alleviate symptoms.
- Avoiding triggers:Identifying and avoiding triggers that provoke hot flashes, such as caffeine, alcohol, or spicy foods, can be helpful.
- Dressing in layers:Wearing loose, breathable clothing in layers allows for easy adjustment during hot flashes.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, hot flashes at night are a complex phenomenon influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding the underlying causes and triggers can empower individuals to manage their symptoms effectively. Whether it’s through lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, or environmental adjustments, there are options available to alleviate the discomfort and improve sleep quality.
Question Bank
What are the most common causes of hot flashes at night?
The primary cause of hot flashes at night is declining estrogen levels during menopause. Other factors include imbalances in the nervous system, sleep disturbances, environmental triggers, and certain medical conditions.
How can I manage hot flashes at night?
There are several strategies for managing hot flashes at night, including wearing loose, breathable clothing, keeping the bedroom cool, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and practicing relaxation techniques.
When should I seek medical attention for hot flashes?
If hot flashes are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, chills, or vaginal bleeding, it’s important to seek medical attention to rule out any underlying health issues.