What is good for hot flashes – Hot flashes, a common symptom of menopause, can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. Understanding what triggers them and exploring effective management strategies is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, treatment options, and lifestyle modifications that can help alleviate the discomfort associated with hot flashes.
From hormone replacement therapy to acupuncture, we explore a wide range of approaches to managing hot flashes. We also provide practical tips on diet, exercise, and stress management to help you find relief and regain control over your well-being.
Definition of Hot Flashes

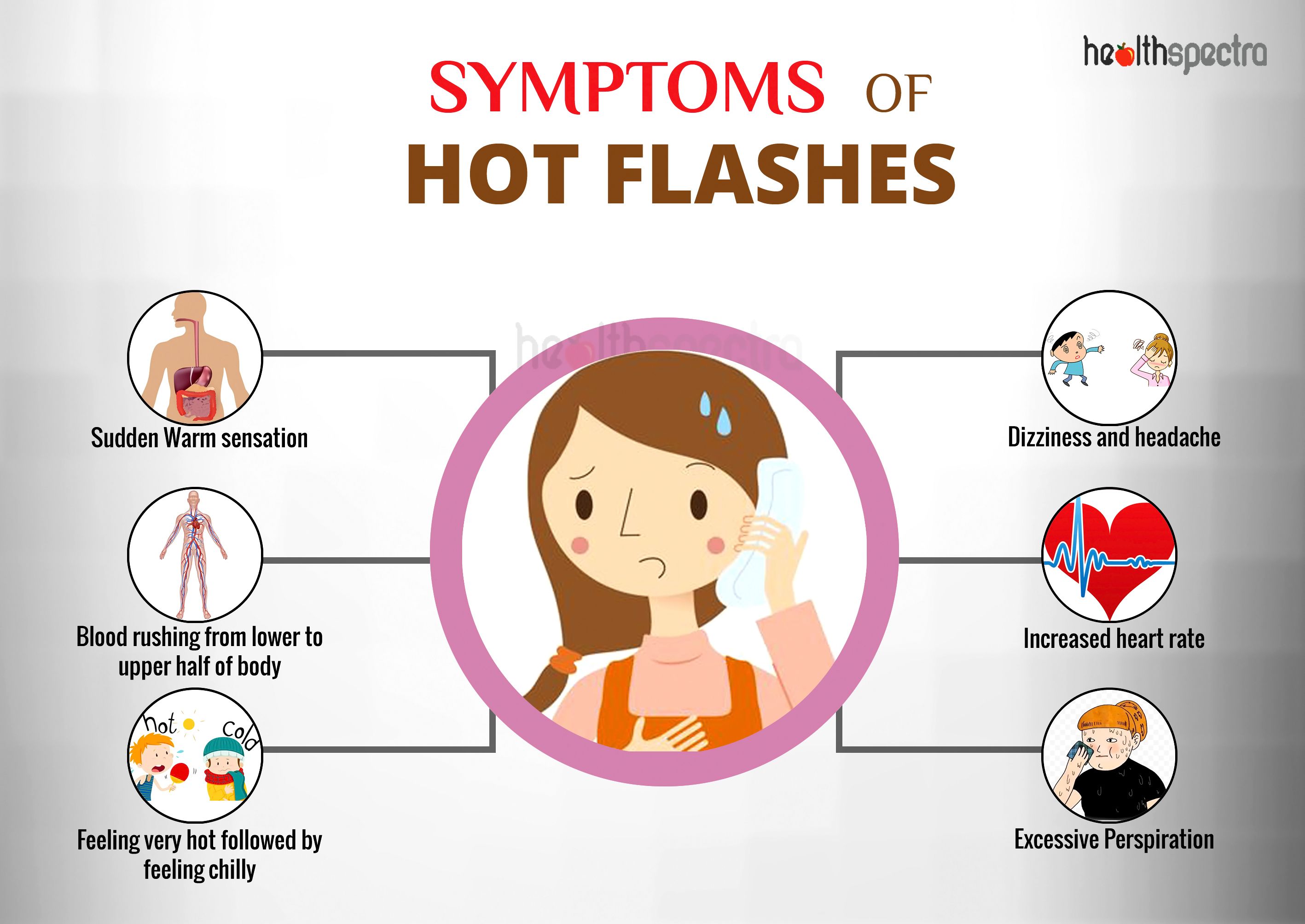
Hot flashes are a common symptom of menopause, a natural transition that occurs when a woman’s ovaries stop producing eggs. They are characterized by a sudden feeling of intense heat and sweating that spreads over the face, neck, and chest.
Hot flashes can be accompanied by other symptoms such as heart palpitations, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Causes and Triggers of Hot Flashes
The exact cause of hot flashes is not fully understood, but they are believed to be related to the decline in estrogen levels that occurs during menopause. Estrogen helps to regulate the body’s temperature, and when levels drop, the body’s thermostat becomes less effective at controlling body temperature.
This can lead to episodes of sudden and intense heat.
Certain triggers can also increase the frequency and severity of hot flashes. These triggers include:
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Spicy foods
- Stress
- Tight clothing
- Smoking
Treatment Options for Hot Flashes
Hot flashes can be a distressing symptom of menopause, but there are several treatment options available to help manage them. These options range from lifestyle modifications to medications, and the best approach will vary depending on the individual’s needs and preferences.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain a healthy weight:Excess weight can worsen hot flashes, so losing weight if necessary can help improve symptoms.
- Avoid triggers:Certain foods and drinks, such as spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol, can trigger hot flashes. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help reduce their frequency and severity.
- Exercise regularly:Exercise can help regulate body temperature and improve overall health, which can help reduce hot flashes.
- Practice stress management techniques:Stress can trigger hot flashes, so finding ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing, can be helpful.
Medications, What is good for hot flashes
Several medications are available to treat hot flashes, including:
- Hormone therapy:Hormone therapy, also known as menopausal hormone therapy (MHT), is the most effective treatment for hot flashes. It involves taking estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progesterone to replace the hormones that are lost during menopause.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs):SSRIs are antidepressants that can also be used to treat hot flashes. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which can help reduce hot flashes.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs):SNRIs are similar to SSRIs, but they also affect norepinephrine levels in the brain. They can be used to treat hot flashes that are not relieved by SSRIs.
- Clonidine:Clonidine is a blood pressure medication that can also be used to treat hot flashes. It works by reducing the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which can help reduce hot flashes.
It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of each treatment option with a healthcare provider before making a decision.
Lifestyle Modifications for Hot Flashes
Lifestyle modifications can effectively manage hot flashes, improving overall well-being. These include dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress management techniques.
Diet
- Consume phytoestrogen-rich foods like soybeans, tofu, and flaxseeds, which can mimic estrogen and reduce hot flash frequency.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol intake, as they can trigger vasodilation and worsen hot flashes.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, especially during and after exercise.
Exercise
- Engage in regular moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or swimming, to improve circulation and reduce stress levels.
- Avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it can raise body temperature and interfere with sleep.
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing during exercise to prevent overheating.
Stress Management
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation to reduce stress and anxiety, which can trigger hot flashes.
- Get enough sleep, as sleep deprivation can worsen hot flashes.
- Consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor if stress is a significant factor contributing to hot flashes.
Complementary Therapies for Hot Flashes
In addition to conventional treatments, several complementary therapies have shown promise in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flashes. These therapies aim to address the underlying hormonal imbalances and stress that can contribute to hot flashes.
One of the most well-researched complementary therapies for hot flashes is acupuncture. Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the release of endorphins, which have pain-relieving and mood-boosting effects. Studies have shown that acupuncture can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of hot flashes, and its effects may last for several months.
Another promising complementary therapy is yoga. Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to promote relaxation and reduce stress. Studies have found that regular yoga practice can reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes, as well as improve overall well-being.
Other complementary therapies that have shown some promise in reducing hot flashes include:
- Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR)
- Tai chi
- Massage therapy
- Herbal remedies, such as black cohosh and red clover
It’s important to note that while these complementary therapies may provide some relief from hot flashes, they should not be considered a substitute for conventional treatments. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any complementary therapy.
Medical Interventions for Hot Flashes: What Is Good For Hot Flashes
Medical interventions play a crucial role in managing hot flashes, particularly when lifestyle modifications and complementary therapies provide insufficient relief. Various medications are available, each with its unique benefits and potential risks.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy (HT) is the most effective medical intervention for hot flashes. It involves administering estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progestin to replace the hormones that decline during menopause. HT can significantly reduce hot flash frequency and severity, as well as improve sleep quality and mood.
However, HT is not suitable for all women, especially those with a history of certain types of cancer, blood clots, or liver disease.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are antidepressants that have been found to be effective in reducing hot flashes. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood regulation and body temperature control. SSRIs are generally well-tolerated, with common side effects including nausea, headache, and sexual dysfunction.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are similar to SSRIs but have a broader range of effects on neurotransmitters, including serotonin and norepinephrine. They have also been shown to be effective in reducing hot flashes, although they may have a higher risk of side effects, such as dry mouth, constipation, and dizziness.
Gabapentin
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that has been found to be helpful in reducing hot flashes. It is thought to work by blocking certain nerve signals that contribute to hot flashes. Gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, with common side effects including dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea.
Clonidine
Clonidine is a blood pressure medication that has been found to be effective in reducing hot flashes. It works by stimulating certain receptors in the brain that help regulate body temperature. Clonidine is generally well-tolerated, with common side effects including dry mouth, drowsiness, and dizziness.
Long-Term Management of Hot Flashes

Managing hot flashes long-term requires a multifaceted approach. It involves monitoring symptoms, adjusting treatment plans, and adopting lifestyle modifications to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
Regular monitoring of hot flash symptoms is crucial to assess the effectiveness of treatment and identify any changes in their patterns or severity. Based on this monitoring, adjustments to treatment plans may be necessary, such as modifying dosages or switching medications.
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating certain lifestyle modifications can complement medical interventions and provide long-term relief from hot flashes. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Avoiding triggers such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods
- Dressing in layers and using fans or air conditioning
- Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or yoga
Conclusive Thoughts
Managing hot flashes requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of this condition. By exploring the various treatment options and lifestyle modifications Artikeld in this guide, you can effectively alleviate the discomfort and regain a sense of balance during this transitionary phase.
FAQ Summary
What causes hot flashes?
Hot flashes are primarily caused by hormonal fluctuations during menopause, specifically a decline in estrogen levels.
What are some effective treatments for hot flashes?
Hormone replacement therapy, antidepressants, and certain supplements have shown effectiveness in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
Can lifestyle changes help manage hot flashes?
Yes, incorporating regular exercise, stress management techniques, and dietary modifications can significantly alleviate hot flash symptoms.